Google is the undisputed king of the internet. Your visibility in this search engine can make or break the success of your endeavor, especially if you operate primarily or fully online.
Moreover, conforming to Google’s demands and following its rules can improve your overall online presence, beyond the search results as well, from user experience to social media presence.
However, it’s difficult to obey the king if you don’t know how it works.
Crawling, indexing, ranking, searches… If you have no or only a vague idea of what this is all about, feel free to join us as we explore the intricacies of how Google works below.
Read on and learn what you need to know not only to up your SEO game but also to enhance your overall online presence.
Key Takeaways
- Google is the most important search engine on the internet. If you want people to find your website, you need to make sure it can be found on Google.
- Google's algorithm is a complex system that you can influence by optimizing your website.
- Google finds and indexes websites by crawling them with Googlebot.
- The search results are personalized and constantly changing based on the user's location, search history, and other factors.
What Is Google Algorithm?
Think about Google as a vast library. It contains all the information that’s been put on the internet – at least 2.99 billion pages and counting.
The Google algorithm is a set of rules that determine which pages from this library will appear on the first page of the search results when you type in a query. In other words, it’s what sorts and serves the results you see every time you search for something on Google.
To do this, Google has what’s called web crawlers or spiders. These software programs scour the internet, following links from one page to another and indexing everything they find on their way. The goal is to visit as many pages as possible and make a copy of them, which will then be stored in Google’s database – the aforementioned library.
The next time you type in a query and hit “enter,” the Google algorithm will compare the keywords in your query with the billions of pages stored in its database. It will analyze and assess them all before returning what it considers to be the most relevant results.
First Things First – Crawling the Web
Google’s mission has always been “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” In order to do so, it needs to find all the websites that exist on the internet and index them. The process of finding these websites is called crawling.
Crawling is done with the help of Googlebot, Google’s web crawler. This software “crawls” the internet similarly like a person would – by following links from one web page to another. When it comes across a page, it reads it and adds it to a queue awaiting to be placed in Google’s index, which is a giant database of all the pages Google knows about.
If you want your website to be found and indexed by Google, you need to make sure it can be crawled.
The first step is to check your robots.txt file. This text file tells Googlebot which pages on your website it should and shouldn’t crawl.
If you don’t have a robots.txt file, Google will assume you don’t mind it crawling everything on your site.
Besides robots.txt, you need to allow anonymous users to browse your website – if you don’t, Googlebot also won’t be able to access it. Bear in mind that it does not log in to anything!
If you don’t want Google to crawl certain pages, you can use the robots.txt file to do so - there are other methods, but let’s stick to only this for now.
Using “Disallow” directive in robots.txt, for example, you might want to prevent Google from crawling your website’s admin pages or sensitive user information.
Here’s an example of a default robots.txt file for Magento website:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /index.php/
Disallow: /*?
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /app/
Disallow: /lib/
Disallow: /*.php$
Disallow: /pkginfo/
Disallow: /report/
Disallow: /var/
Disallow: /catalog/
Disallow: /customer/
Disallow: /sendfriend/
Disallow: /review/
Disallow: /*SID=
The second step to making sure your website can be crawled is to have pages link to each other.
Here’s an example of a crawl map for a small website:
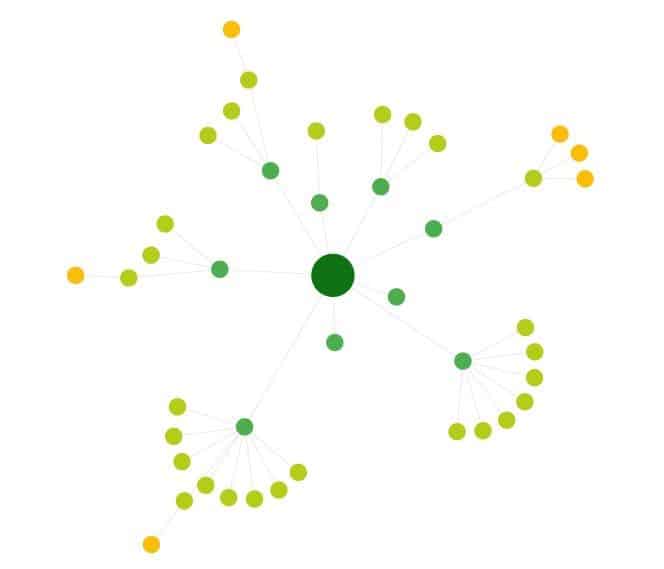
The dots represent pages, with the greenest one in the center being the site’s homepage. Little lines between the pages represent links.
To help Googlebot discover all the pages on your site, you may create a sitemap.
A sitemap is a file containing a list of all the pages on your website. You can submit your sitemap to Google through the Google Search Console.
This will help Google find all the pages on your website, but does not guarantee that they will be indexed! As much as you can help pages to appear in the index, this decision is Google’s and Google’s only.
A good-to-have thing helping your website get properly crawled, is structured data. It’s code that helps Google better contextually understand the content on your website.
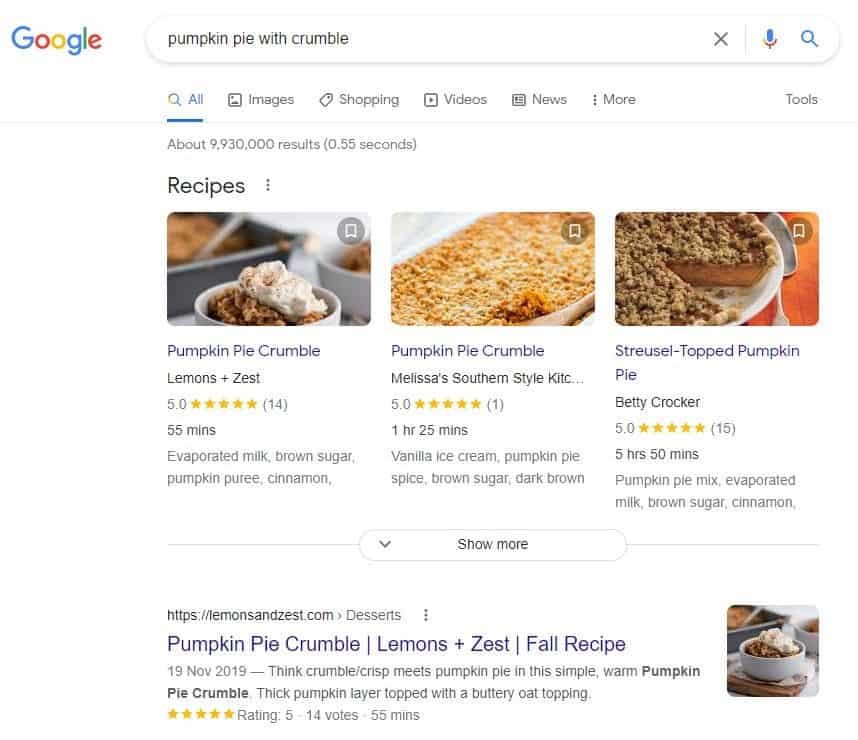
For example, if you have a recipe on your website, you can use structured data to tell Google what the ingredients are, what the cooking time is, and so on.
Adding structured data to your website is optional, but it might really help you stand out in the search results:
Crawling Leads to → Indexing
Once Googlebot has found and crawled your website, it will place your pages in a queue to add them to the Google index. The index is a giant database of all the pages that Google knows about. When someone performs a search, in simple terms, Google will look through the index to find the pages that are relevant to the search.
If your website is not in the index, it will not appear in the search results! This is why it’s essential to make sure that your website can be crawled and that all your pages are indexed.
To index and display your website in search results, Google needs to understand what your website is about.
It does this by looking at the title, metadata, and content of your pages, including texts, images, and videos. The search engine also looks at the structure of your website as a whole, and also at the way your pages are linked with each other.
Google decides which pages to index and which to ignore by looking at their content, the links pointing to them, and other factors.
Google uses its ranking system to decide which pages to show first in the search results. It is a complex algorithm that considers many factors, and is constantly being updated and tweaked.
But, you can say that it generally relies on a few key factors, including:
- Relevance: How well does the content on the page match the query?
- Authority: How trustworthy and authoritative is the website?
- Links: How many other websites link to the page?
- Freshness: How recently was the content on the page updated?
- User experience: How easy is it to use the website and find the content you're looking for?
- Speed: How quickly does the page load?
- Mobile-Friendliness: Does the page work well on mobile devices?
- RankBrain: How all the information across the pages is interconnected?
These are just a few of the factors that Google takes into account when ranking pages, but they give you a general idea of the types of things that Google is looking for.
The Google ranking system is constantly changing, so it’s vital to keep your website up-to-date and add new content regularly.
As a rule of thumb, the more relevant and high-quality content you have, the higher your website will rank in the search results.
The Magic in Practice – Search Result Ranking
Now that you know how crawling and indexing work, let’s take a look at what happens when a search happens on Google.
If you type a query into the Google search bar, Google will look through its index to find the pages that are relevant to the query. It will then use its ranking system to decide which of these pages to show first in the search results.
Google Determines Context
First, Google will try to understand the context of the query. It uses a number of signals to determine it, including:
- the location of the person doing the search,
- the time of the search,
- the history of the person's searches,
- the language.
For example, if someone in New York searches for “pizza,” Google will assume that they are looking for a pizza place in New York. If someone searches for “pizza” at 3 a.m., Google may prioritize late-night pizza delivery places.
It also considers the device you use to perform the search. If you search for “pizza” on your smartphone, it will show you mobile-friendly websites first.

Google Uses AI Algorithms to Uncover User's Intent
After understanding the context of the query, Google will try to understand the user's intent. That is, what does the user want to accomplish with their query?
There are several types of intent, with the main being:
- commercial intent: the user is looking to buy something,
- informational intent: the user is looking for information,
- transactional intent: the user is looking to do something, such as make a reservation or buy a ticket,
- navigational intent: the user is looking for a specific website.
Google itself recommends the following user intent distribution it in its Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines:

So, why does Google need its high-end AI algorithms to understand the user's intent?
The answer is simple – to give the user the best possible results, regardless of the language they use, mistakes they may make, and so on.
To achieve this, Google uses different techniques, including:
- natural language processing,
- semantic analysis,
- contextual analysis.
For example, the RankBrain algorithm determines the relationship between words, while the BERT algorithm understands the context of a sentence.
EAT and YMYL
Google also uses what is known as the EAT principle to rank pages. EAT stands for “expertise,” “authoritativeness,” and “trustworthiness.” Google looks for pages that have all three of these qualities.
- Expertise refers to the author’s knowledge of the subject. To show expertise, the author needs to be an expert on the subject and demonstrate a deep understanding of the topic.
- Authoritativeness is about reputation. Google looks for web pages that are written by authoritative sources. Authority can be shown through things like awards, mentions, quotations, links, etc.
- Trustworthiness is related to accuracy and reliability. Google looks for web pages that are free of errors and present accurate information, quote sources correctly, link to established authorities, etc.
The EAT principle is especially important for pages that deal with what Google calls “your money or your life” (YMYL) topics.
These are topics that can directly impact a person’s wellbeing, such as health, financial, or legal advice. Google is especially strict when it comes to this type of content.
To rank well for YMYL queries, you need to show that you have a profound understanding of the topic and that you can be trusted to give accurate and reliable information.
To achieve this, you need to, for example:
- have a well-designed website,
- have an About page that tells users who you are and what are your qualifications,
- have a Privacy Policy and Terms of Service that are easy to find and understand,
- use reputable sources,
- cite your sources correctly,
- avoid spelling and grammar errors,
- have a high-quality, mobile-friendly website.
On-Page and Off-Page Ranking Factors
There are many other factors that Google considers when ranking pages. These can be divided into two main categories: on-page ranking factors and off-page ranking factors.
On-page ranking factors are factors that are directly under your control, such as the title and meta tags of your pages, the keyword density, the relevance of your content, etc.
Off-page ranking factors are factors that are not directly under your control, such as the number of links pointing to your website, the quality of these links, the social media signals, etc.
Search Engine Results Page (SERP)
After Google has crawled and indexed the pages on your website and decided which ones to show in the search results, it will generate a SERP (search engine results page).
This is the page you see when you perform a search on Google. It contains the list of results that Google has determined to be the most relevant to your query.
The SERP also contains other information, such as ads, the Knowledge Graph, featured snippets, and so on.
The search results are not static!
Google personalizes the search results for each user.
They are constantly changing based on the user’s location, search history, and other factors.
This is why you might see different results when someone else does the exact same search.
Conclusion
This is just a brief overview of how Google works. Now, you know that Google finds and indexes websites by crawling them with Googlebot. You also know that the search results are personalized and that you can influence them by optimizing your website.
Google’s algorithm is a complex system, and there is a lot more to it than what we’ve covered here.
However, this should give you a good idea of the basics of how Google works and how you can influence the search results for your website.
Google is the most important search engine on the internet. If you want people to find your website, you need to make sure it can be found on Google.
Keep these things in mind as you continue to work on your website and your SEO. If you have any questions, feel free to contact us or leave a comment below!






