Among all the tweaks and upgrades Google introduced to its core algorithm throughout the years, none might be more important than RankBrain.
This machine-learning artificial intelligence system truly revolutionized the way Google Search operates, allowing it to handle more never-before-seen search queries.
What some people glossed over in 2015 has become a turning point in Google's search engine history. RankBrain, announced in the fall of that same year, has remained active ever since — and its importance only grew with time.
Nowadays, the widespread impact RankBrain has on content and search engine optimization (SEO) is hard to measure.
According to Google, it is the third most important ranking signal, but the true extent of its inner workings is shrouded in mystery.
Here is a thorough explanation of how RankBrain works and why it is so crucial for SEO.
Key Takeaways
- RankBrain is a machine-learning, artificial intelligence system Google uses to process search queries. It is the third most important ranking signal for Google.
- RankBrain transforms words in a search query into word vectors — a computer way of figuring out the word's meaning. If words are located close to each other in the vector space, their meanings are similar.
- Thanks to this process, RankBrain can deal with ambiguous search queries. Even if it does not fully understand them, it can make a pretty good guess.
- If it encounters a word it has never seen before, it determines its meaning based on contextual information and similar language.
- If the user is satisfied with the search results, the system has fulfilled its goal. If not, it utilizes the feedback it received to do better next time.
What Is RankBrain?
RankBrain is a machine-learning, artificial intelligence system Google uses to process search queries. It is innovative because Google needed to hand-code every change made in its algorithm before implementing this solution. As you can imagine, it was a long and tedious process.
RankBrain changes that.
Today, besides manual adjustments in code made by Google's engineers, AI technology constantly runs in the background, gathering feedback and rolling out algorithm improvements if needed. It is a significant step towards creating a self-regulating system that will automatically detect issues and enforce counter-measures to solve them.
In fact, many digital marketing specialists already state that Google’s algorithm is a self-adjusting one.
In its practical application, RankBrain follows in the footsteps of the 2012 Hummingbird Update — an all-around transformation of Google's algorithm to promote writing in natural language, putting more emphasis on context and meaning over individual keywords.
RankBrain's priorities are straightforward — it "guesses" what the user wants to see, delivers the results it deems suitable, and analyzes the reaction.

Source: https://backlinko.com/google-rankbrain-seo
If the user is satisfied with the search results, the system has fulfilled its goal. If not, it utilizes the feedback it received to do better next time.
How RankBrain Works
So, what does RankBrain do to deliver such outstanding results?
Paradoxically, it makes things more complex to understand search queries better.
RankBrain transforms words in a search query into word vectors — a computer way of figuring out the word's meaning. If words are located close to each other in the vector space, their meanings are similar.
Thanks to this process, RankBrain can deal with ambiguous search queries. Even if it does not fully understand them, it can make a pretty good guess.
If it encounters a word it has never seen before, it determines its meaning based on contextual information and similar language.
Every word in the world has a position and a proximity to other words.
Google can map queries in search in that space, so you get the proximity and distance of different queries.
Instead of operating on mere keywords alone, the post-RankBrain Google algorithm has an added depth to it.
This extra depth allows it to compare the words' similarities regarding their meaning — all done within the virtual space.
Regardless, this method is not without its flaws.
Here’s an example of word2vec, which can also calculate the distance and relationship between the words:
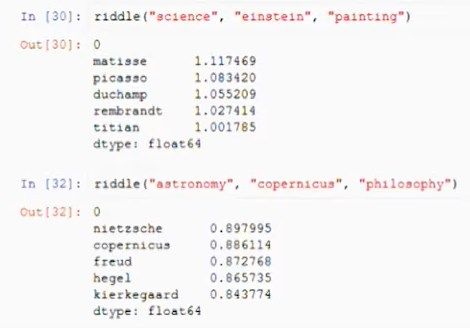
Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AGgCqpouKSs
RankBrain's Limitations
The main limitation of using word space models is that words with multiple meanings are conflated into a single representation.
It creates a problem with deciphering what words like "crane," "club," and "chair" actually mean in a given context.
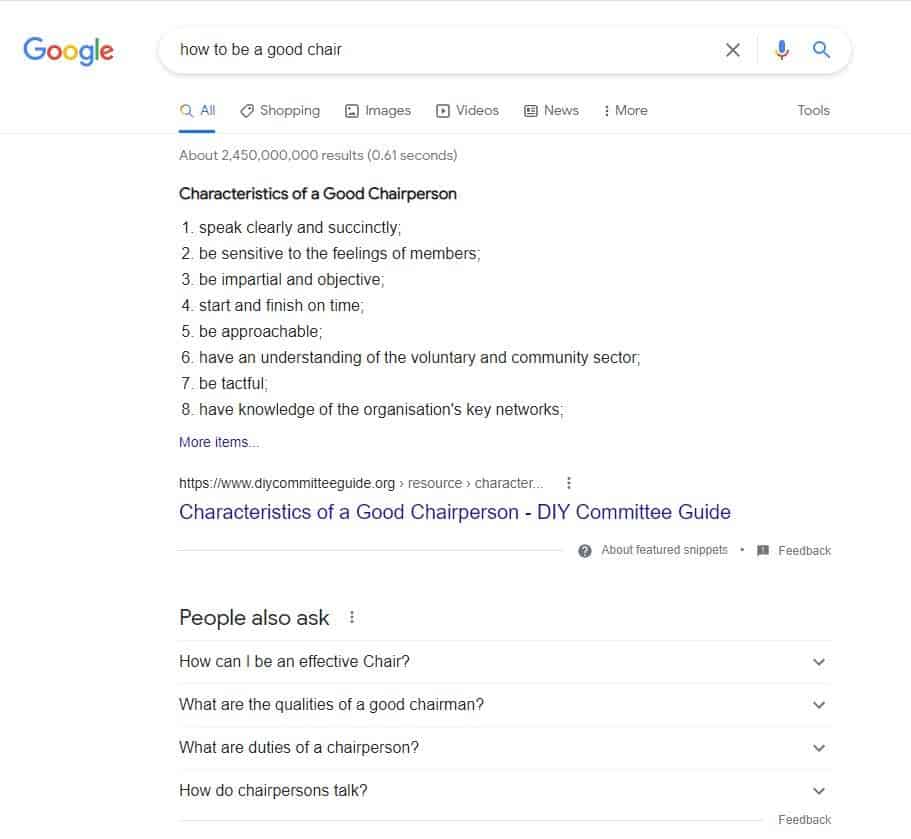
Let's say you enter the sentence "how to be a good chair" into the search box.
Following only the instructions provided by the word space model, the system might have difficulties deciding whether by "chair" you mean:
- a separate seat for one person, typically with a back and four legs
 ,
, - the person in charge of a meeting or an organization
 .
.
At this point, the algorithm plays a guessing game, hoping to find a satisfying answer.
It is not guaranteed you will receive the information you are looking for.
Fortunately, Google has addressed this problem by releasing Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) in 2018.
It uses a word's context to understand its meaning, so polysemy and homonymy are no longer issues users need to worry about.
Going back to RankBrain, it takes the feedback it receives from users to "learn" what they want to see.
For example, when we type the sentence "how to be a good chair" into the search box today, we can notice that the algorithm has already learned we refer to the second of the presented meanings.
Thus, it presents a list of articles like "Characteristics of a Good Chairperson" instead of the ones explaining what a good chair should be made of and why it is an essential piece of furniture for your living room.
How Rankbrain Collects and Uses Feedback
So far, so good, but you might ask: how does RankBrain actually collect feedback?
It is a perfectly valid question!
Nonetheless, the answer to it is complex and multi-faceted.
At its core, RankBrain cares the most about user experience (UX).
Because of this fact, it pays close attention to a set of variables we know as user experience signals.
Among these UX signals, four are critical in evaluating content quality — all of which RankBrain uses to deliver its on-point results:
- Dwell Time,
- Organic Click-Through Rate,
- Pogo-sticking,
- Bounce Rate.
Let's examine these factors one by one to gain a better understanding of RankBrain's feedback-gathering systems.
Dwell Time
In simple terms, dwell time is the amount of time you spend on a page before returning to the search engine results page (SERP).
Many SEO experts consider it one of the crucial Google ranking factors.
RankBrain can determine how successful its top propositions were by looking at dwell time.
If the user spends a considerable amount of time on a given page, RankBrain might boost its ranking.
Conversely, if they quickly abandon the site, the algorithm can conclude users were unhappy with that result and that the content present on the site is subpar.
In consequence, it can lower its placement in SERPs.
Organic Click-Through Rate
Organic click-through rate (CTR) refers to the number of people who click on the presented results in SERPs.
The more people click on a particular link, the higher its organic CTR.
This element matters to RankBrain because it shows how accurate it was in its response to the search query.
If one of its suggestions is constantly overlooked, the system might determine it is time to switch things up and put another page in its place.
Overall, pages with a higher than average CTR might expect a ranking boost.
At the same time, pages that underperform in this department will most likely receive lower rankings and, in turn, less traffic.
Pogo-sticking
Pogo-sticking is when the user "jumps" from one page to another, searching for valid information.
If many people "pogo-stick" from a given page, it is a signal for RankBrain to place it lower in SERPs.
On the other hand, if people do not return to search results after entering a specific page, it makes the page more valuable in RankBrain's eyes.
Bounce Rate
Finally, we need to talk about the bounce rate.
It is the percentage of visitors that leave a page without taking action (e.g., buying a product or filling out a form).
While this element might seem similar to dwell time, they are not identical.
Dwell time is solely focused on the amount of time someone spends at a site.
On the contrary, bounce rate cares only about the act of "bouncing" — returning to search results without doing anything more on a given page.
Whether you spend a few seconds or half an hour during the process does not matter.
What matters is if you did anything else besides reading the content before going back.
Why RankBrain Matters
Okay, so now we know how RankBrain works. But what difference does it make in terms of search engine optimization?
Apart from making Google's algorithm better at handling about 15 percent of all searches, the introduction of RankBrain requires SEOs to reconsider their approach.
The post-RankBrain era does not reward stuffing your articles with tons of keywords nor creating hundreds of pages where each one of them is optimized around a slightly different keyword.
Here is how RankBrain has influenced the SEO landscape:
Switching From Long-Tail Keywords to Medium-Tail Keywords
With RankBrain's improved understanding of words and their meanings, creating a separate page for specific long-tail keywords is inefficient.
It is much better to focus on medium-tail keywords, which are still relatively easy to rank for yet are not as vague as long-tail ones.
What do we mean by that?
Before the introduction of RankBrain, Google used to rank long-term keywords separately, even if they were about the same topic.
Today, the algorithm understands they mean basically the same thing.
As a result, it shows similar results, whether we type in the first or the second long-tail keyword.
What matters to Google's core algorithm the most is the meaning carried by words used in the search query.
And, as it grew to understand this meaning better than ever before, creating more than one page for each meaning has become no longer needed.
Medium-tail keywords, however, are still valuable targets.
Due to their middle-of-the-pack search volume and high ranking potential, they are excellent choices to optimize your webpage around.
Optimizing for User Experience Signals
Another vital change RankBrain brought to the table is encouraging web admins to pay more attention to user experience.
While before RankBrain, they could get away with delivering mediocre experiences, now it is not the case.
Simply put, if users do not enjoy their stay on your site, you cannot expect it to rank high in SERPs.
For example, having high organic CTR and low bounce rates has become more crucial than ever.
This situation leads SEOs to optimize for user experience signals we mentioned earlier.
You can do many things to improve your user experience:
- Create Titles Packed With Emotions
One of the best ways to get people to click on your article is by having an eye-catching headline.
Creating titles that burst with emotions can boost your CTR and improve your page's chances of ranking high in SERPs. - Make Your Website Look Good
Have you even clicked on an article with a catchy title only to be greeted with an outdated design and terrible font choice?
If so, you know how big of a role the website's looks can play in making a reader hang out for longer.
If you make your website design fabulous, you can significantly reduce pogo-sticking and boost your dwell time. - Use Numbers in Your Titles
Another useful CTR-boosting trick is to put some numbers in your titles.
This way, you can share relevant data from the get-go with your readers, grabbing their attention and increasing the chance they will click on the article to learn more about the subject. - Create Superb Content
While it is easier said than done, data-driven and well-written content can push your webpage above the fold and make it stand out.
Because of this, you might want to devote more time and effort to ensure that each article on your site is truly worthy of being there. - Do Not Forget About Meta-Descriptions and Alt-Text
Both meta-descriptions and alt-text play a key role in helping Google understand what your page has to offer.
You cannot forgo adding these elements to your content, as it is a critical way to keep Google up to date with the context around your web pages and articles.
The Bottom Line
All improvements to Google's search engine have been done with one goal in mind — providing the people who use it with the most relevant content possible and making their search experiences more manageable.
RankBrain is not different in this regard.
Yet, it was the first major step Google took to streamline this process from their perspective.
So far, handing over the wheel to AI has proven to be an advantageous decision — both for the company and internet users.
Thanks to RankBrain's incredible ability to convert words into word vectors, we can enjoy reading well-written, exciting articles instead of keyword-stuffed blog posts with little to no actual value.
What the future holds for RankBrain remains to be seen.
Either way, it will be fascinating to watch how the algorithm adapts to suit the needs of the modern-time consumer.






